
Memory and Swap History provides the same graphical information but for your system’s memory, both physical and swap.In addition, the right side of the widget includes the current percentage usage for each CPU. Each line on the graph represents one of your system’s CPUs. CPU History displays a graph of CPU usage over the last minute.You can refer to the screenshots in the What is gtop? section above to follow along. What follows is a breakdown of the parts, or widgets, of the gtop display. When you run gtop it immediately starts showing your system’s usage and process information. One advantage of gtop is that, despite its graphical display, it is a straight-forward system monitoring application. Use the -g option to install gtop as a global system package. You can then verify your npm installation with using the -version option.
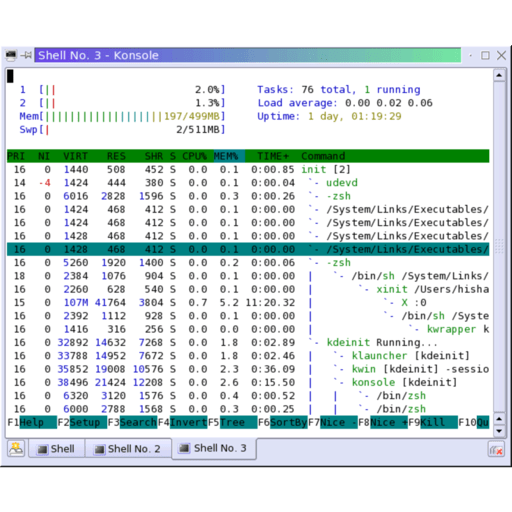
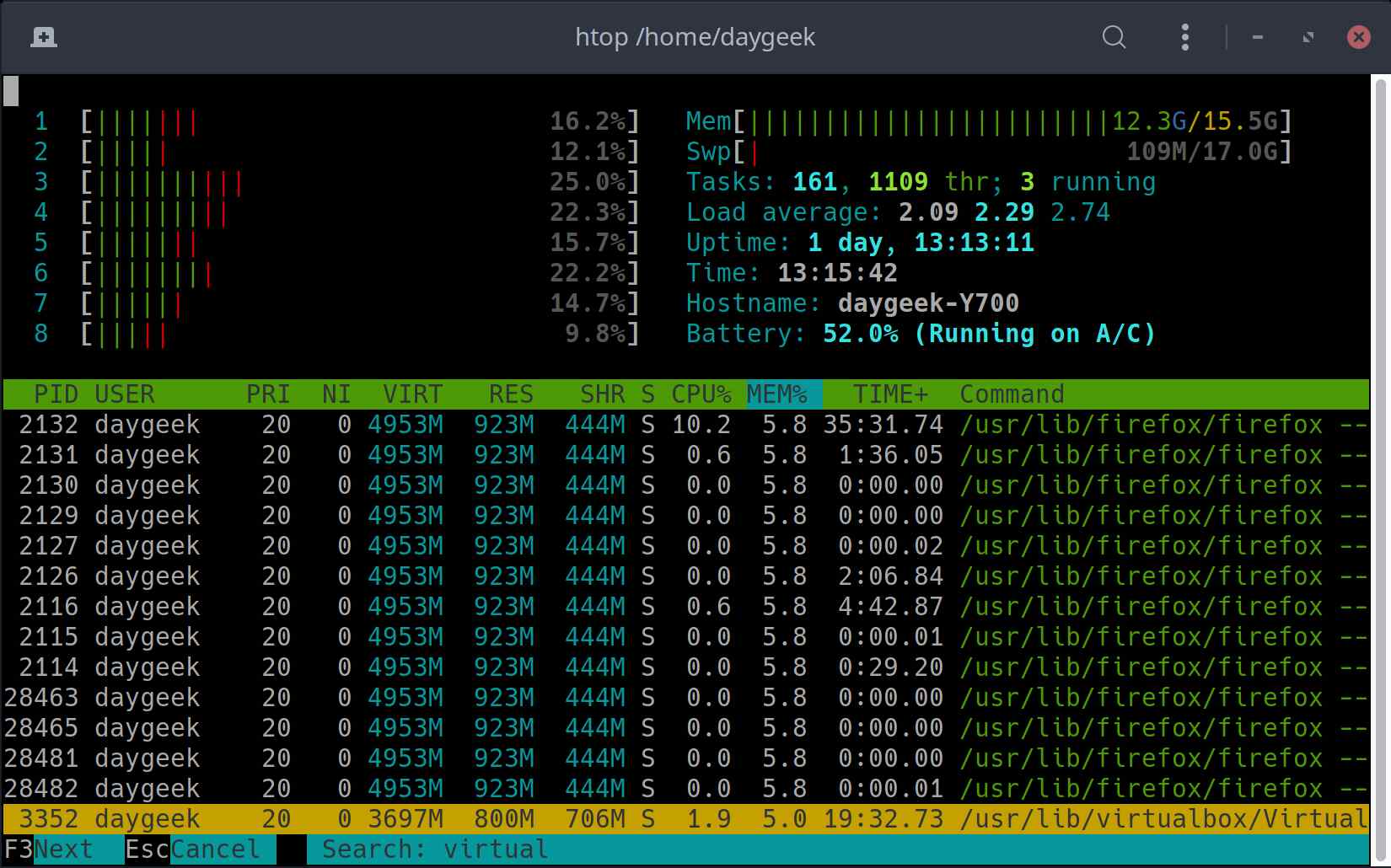
You may want to consult the nvm installation guide and replace v0.38.0 below with the latest version you see in the guide. You can use the following commands to install nvm and then use it to install the current version of Node (which includes npm). This section shows you how to install npm, using the Node Version Manager (nvm), and then, how to install gtop. In order to install gtop you need to instal the Node Package Manager (npm). Take a look at the screenshots below, which contrast the displays of top, htop, and gtop. Gtop employs distinct coloring in its displays, making it all the more readable, too. With gtop, you get various graphs in widgets that break up your monitoring into visual sections. But unlike htop, which still focuses on listing processes, gtop seeks to provide an almost entirely graphical representation of the system’s usage information. Gtop takes up the graphical direction of htop. Htop adds vertical and horizontal scrolling, mouse input, more information about processes, and additional features. If you are unfamiliar, top is a command included by default on most Unix systems for viewing running processes and system usage information. Gtop is built on the precedent of htop, which aims to be a more interactive and graphical version of top. Alongside that information, you get a list of running processes with statistics about their CPU, and memory consumption. Gtop displays your system’s memory, CPU, and disk usage at a glance in an easy-to-read visual layout. Gtop is a graphical system monitoring dashboard for your terminal. If you’re not familiar with the sudo command, see the Linux Users and Groups guide. Commands that require elevated privileges are prefixed with sudo. The steps in this guide are written for non-root users.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
